Difference between revisions of "Adaptive VIBE"
From PAWS Lab
(→Publications) |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
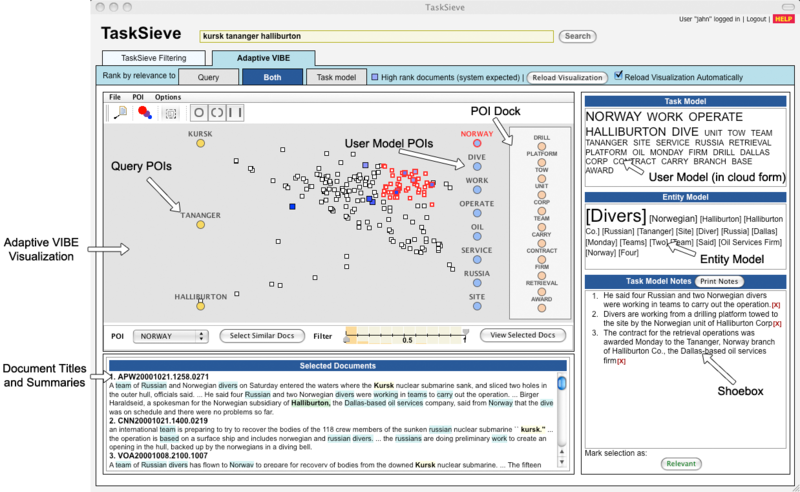
| − | + | Adaptive VIBE is a variation of VIBE, a reference point-based spatial visualization algorithm. It supports the visualization of user models as well as usual documents. User model is displayed as a separate group of POIs (Points of Interests or reference points). Because it is located in distant positions from the query POIs, users can mediate visually between their explicit interests (queries) and the system estimated interests or search contents (user models). | |
| − | [[Image:VisualTaskSieve.png| | + | |
| + | [[Image:VisualTaskSieve.png|800px|center|Adaptive VIBE integrated into the TaskSieve system]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Publications == | ||
| + | <onlyinclude> | ||
| + | * Ahn, J., and Brusilovsky, P. (2009) '''Adaptive Visualization of Search Results: Bringing User Models to Visual Analytics'''. Information Visualization 8 (3), 167-179. | ||
| + | * Ahn, J., and Brusilovsky, P. (2007) '''From user query to user model and back: Adaptive relevance-based visualization for information foraging'''. In: T. Y. Lin, et al. (eds.) Proceedings of the 2007 international conference on Web Intelligence, WI '07, Silicon Valley, CA, USA, November 2-5, 2007, IEEE, pp. 706-712. | ||
| + | * Ahn, J.-w., Brusilovsky, P., and Sosnovsky, S. (2006) '''QuizVIBE: Accessing Educational Objects with Adaptive Relevance-Based Visualization'''. In: T. C. Reeves and S. F. Yamashita (eds.) Proceedings of World Conference on E-Learning, E-Learn 2006, Honolulu, HI, USA, October 13-17, 2006, AACE, pp. 2707-2714. | ||
| + | * Brusilovsky, P., Ahn, J., Dumitriu, T., and Yudelson, M. (2006) '''Adaptive knowledge-based visualization for accessing educational examples'''. In: B. Ebad, et al. (eds.) Proceedings of Information Visualization, London, UK, July 5-7, 2006, IEEE, pp. 142-147 | ||
| + | </onlyinclude> | ||
Latest revision as of 02:19, 11 December 2009
Adaptive VIBE is a variation of VIBE, a reference point-based spatial visualization algorithm. It supports the visualization of user models as well as usual documents. User model is displayed as a separate group of POIs (Points of Interests or reference points). Because it is located in distant positions from the query POIs, users can mediate visually between their explicit interests (queries) and the system estimated interests or search contents (user models).
Publications
- Ahn, J., and Brusilovsky, P. (2009) Adaptive Visualization of Search Results: Bringing User Models to Visual Analytics. Information Visualization 8 (3), 167-179.
- Ahn, J., and Brusilovsky, P. (2007) From user query to user model and back: Adaptive relevance-based visualization for information foraging. In: T. Y. Lin, et al. (eds.) Proceedings of the 2007 international conference on Web Intelligence, WI '07, Silicon Valley, CA, USA, November 2-5, 2007, IEEE, pp. 706-712.
- Ahn, J.-w., Brusilovsky, P., and Sosnovsky, S. (2006) QuizVIBE: Accessing Educational Objects with Adaptive Relevance-Based Visualization. In: T. C. Reeves and S. F. Yamashita (eds.) Proceedings of World Conference on E-Learning, E-Learn 2006, Honolulu, HI, USA, October 13-17, 2006, AACE, pp. 2707-2714.
- Brusilovsky, P., Ahn, J., Dumitriu, T., and Yudelson, M. (2006) Adaptive knowledge-based visualization for accessing educational examples. In: B. Ebad, et al. (eds.) Proceedings of Information Visualization, London, UK, July 5-7, 2006, IEEE, pp. 142-147