Difference between revisions of "Aggregate"
From PAWS Lab
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
* The figure shows several different Content apps (QuizJet, QuizPet, Webex, etc.). Each of these applications are integrated in 2 ways: | * The figure shows several different Content apps (QuizJet, QuizPet, Webex, etc.). Each of these applications are integrated in 2 ways: | ||
| − | ** The | + | ** The content application provides a service to list all the available content. This service implement the [https://github.com/PAWSLabUniversityOfPittsburgh/mastery-grids/blob/master/documentation/Content_Brokering_API_2016_01_21.pdf content brokering specification], which defines how the content can be discovered in JSON format. |
This architecture supports several kinds of open student modeling, social comparison, and recommendation. The architecture fulfills a major objective, portability, which is the ability to be integrated to other systems with little set up and modification. The architecture is modular and includes different software components as follows: | This architecture supports several kinds of open student modeling, social comparison, and recommendation. The architecture fulfills a major objective, portability, which is the ability to be integrated to other systems with little set up and modification. The architecture is modular and includes different software components as follows: | ||
Revision as of 18:07, 4 April 2016
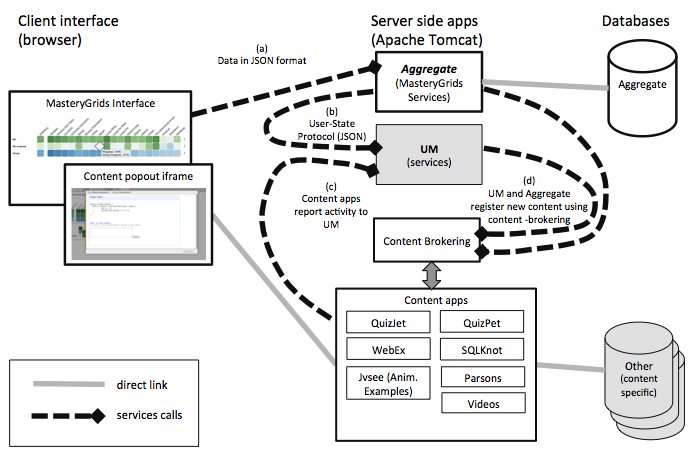
We developed an adaptive social learning architecture Aggregate to support Mastery Grids Interface. We design this architecture to integrate content from diverse sources. The explanation of the procedures and links to associated resources are given below.
- Mastery Grids Interface receives all the information to display (this is course structure, links to content and progress levels of the learner and the group of learners) from services hosted in Aggregate (a in the diagram). This information is passed in JSON format.
- To let Mastery Grids know the level of progress of the learners in the topics and the content, Aggregates call services from a User Model (UM in the figure). See point b) in the figure. These services are documented in User State Protocol
- The figure shows several different Content apps (QuizJet, QuizPet, Webex, etc.). Each of these applications are integrated in 2 ways:
- The content application provides a service to list all the available content. This service implement the content brokering specification, which defines how the content can be discovered in JSON format.
This architecture supports several kinds of open student modeling, social comparison, and recommendation. The architecture fulfills a major objective, portability, which is the ability to be integrated to other systems with little set up and modification. The architecture is modular and includes different software components as follows:
- frontend user-system interaction interface, the Mastery Grids Interface
- backend Aggregate services communicating between the main interface and user modeling services ==> source code
- backend user modeling, personalization (recommendation, navigation support) services
- backend content providing applications
An overall architecture of the system can be sen in the following figure.