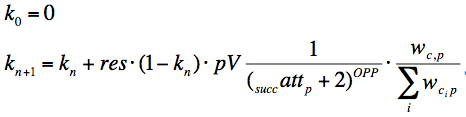Difference between revisions of "CUMULATE parametrized asymptotic knowledge assessment"
From PAWS Lab
(→Computation) |
(→Computation) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
* the initial level of knowledge, speed of knowledge growth, and penalty for repetitive (correct) solutions to the problem - are now adjustable parameters | * the initial level of knowledge, speed of knowledge growth, and penalty for repetitive (correct) solutions to the problem - are now adjustable parameters | ||
[[Image:CUMULATE parameterized asymptotic knowledge assessment.png]], where | [[Image:CUMULATE parameterized asymptotic knowledge assessment.png]], where | ||
| − | * ''Ko'' - is the starting level of knowledge, Ko ∈ [0, 1] | + | * ''Ko'' - is the starting level of knowledge, ''Ko'' ∈ [0, 1] |
* ''res'' - result of user action (0 -error, 1 - correct); | * ''res'' - result of user action (0 -error, 1 - correct); | ||
* ''Wc,p'' - is a weight of concept ''c'' in problem ''p'' | * ''Wc,p'' - is a weight of concept ''c'' in problem ''p'' | ||
* Σ''Wc,p'' - is the sum of weights of all concepts in problem ''p'' | * Σ''Wc,p'' - is the sum of weights of all concepts in problem ''p'' | ||
* ''<sub>succ</sub>att<sub>p</sub>'' - is a number of successful solutions to problem ''p'' prior to current attempt | * ''<sub>succ</sub>att<sub>p</sub>'' - is a number of successful solutions to problem ''p'' prior to current attempt | ||
| − | * ''pV'' - speed of knowledge growth parameter | + | * ''pV'' - speed of knowledge growth parameter, ''pV'' ∈ [0, 1] |
| − | * ''OPP'' - over-practicing parameter, controlling the penalty for repetitively solving one problem (correctly) | + | * ''OPP'' - over-practicing parameter, controlling the penalty for repetitively solving one problem (correctly), ''OPP'' ∈ [0, 1] |
=Examples= | =Examples= | ||
Revision as of 20:37, 8 April 2009
Parameterized asymptotic knowledge assessment algorithm is an attempt to overcome shortcomings of its non-paramterized version.
Contents
Computation
The formula below is used to update the knowledge levels of concepts (c) addressed in a problem (p). This formula reflects the following principles (identical to the predecessor algorithm).
- there are several domain concepts (knowledge items, rules, productions) involved in solving a problem; the knowledge of each of them is updated proportionally to the others
- knowledge is updated only upon correct user answers, there is no penalty for errors
- solving a problem correctly multiple times will result in diminishing update (growth) of the knowledge level of the concepts as the number of successes grows
in addition:
- the initial level of knowledge, speed of knowledge growth, and penalty for repetitive (correct) solutions to the problem - are now adjustable parameters
- Ko - is the starting level of knowledge, Ko ∈ [0, 1]
- res - result of user action (0 -error, 1 - correct);
- Wc,p - is a weight of concept c in problem p
- ΣWc,p - is the sum of weights of all concepts in problem p
- succattp - is a number of successful solutions to problem p prior to current attempt
- pV - speed of knowledge growth parameter, pV ∈ [0, 1]
- OPP - over-practicing parameter, controlling the penalty for repetitively solving one problem (correctly), OPP ∈ [0, 1]
Examples
soon